Online Course
NURS 787 - Theoretical Foundations of Teaching and Learning Course
Module 5: Objectives, Leveling, and Alignment
Behavioral Objectives

A correctly stated behavioral objective has an audience, an action verb, conditions, and criteria. Here is an example:
After completing the unit on dosage and solution, the student must complete a 100 item multiple-choice test at the 85% level within the one-hour examination period.
- The action verb = complete a 100 item multiple choice test
- The condition = after completing the unit on dosage and solution multiple-choice test
- The criteria = at the 85% level within the one hour examination period
The audience = the student
This is called the long method of writing objectives. It is complete and specific but somewhat cumbersome. There is a short method of objective writing. It focuses primarily on the action. This type of objective is still considered correct if it has an appropriately stated action verb that is specific and measurable. The short method of writing the above objective might look like this:
At the end of this course, the student will pass the medication exam with a score of 85%.

Two issues are involved in writing objectives
One isthe specificity and the other islevelof objective.
Robert Mager suggests a method of writing objectives using numerous and specific objectives. He suggests outlining the content to be taught within the objectives. An example is to use course and unit (or module) objectives. Course objectives are broad and unit objectives are specific.
The module, unit, or lesson objectives must support or align with the course objectives, which in turn should align with the overall program objectives. This alignment adds structure and balance to teaching and learning. Much like a car is difficult to control and predict when the wheels are out of alignment, our classes can quickly go off track when objectives and activities are not aligned. Later in the module we’ll also discuss how content, objectives, teaching strategies, and assessment must also align to help learners reach their goals.
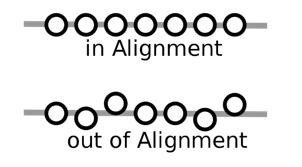
Example #1 –
An overall program objective example may be:
Students will gain requisite knowledge and skills to positively influence the health of families and communities.
A broad course objective example follows.
The student will describe a model of health education that relates to his/her own definition of health.
The specific unit objectives could be:
By the end of the unit/module the student will:
- Compare and contrast definitions of health
- Define the following terms related to health: health promotion, illness prevention, and health maintenance
- Describe four perspectives of health: eudemonistic, adaptive, role performance, and clinical
- Define the term models and theories
- Explain the use of models and theories in health
- Explain Precede-Proceed Model of health
- Explain the Health Belief Model
- Explain the Health Promotion Model
- Explain the natural history of disease
Example #2 –
Tyler suggested another method of writing objectives. Tyler's method of writing behavioral objectives is to usemore global terms, chunking content pieces together within the objectives. The teaching unit's content outline is much more specific.
The student will:
- Apply the nursing process to clients experiencing stress
- Discuss the theories of stress
In this example, a detailed content outline will be needed to guide the learner's focus.
Example #3 –
The final issue is leveling objectives. Learning objectives that are written for new or novice students or learners newly introduced to new learning material should be at a lower level and experienced learners should be challenged with higher level objectives.
This is an example of the progression of levels of objectives in a two-day workshop for nurse educators on e-Learning for Health and Health Care.
Module 2
Purpose: Introduction to web-based learning
Objective: The learner will:
- Describe the history of web-based learning
- Identify the unique characteristics of online learning environments
- Identify the advantages and disadvantages on learning online
- Explain the principles of sound education online
Module 8
Purpose: To design an online learning environment
Objective: The learner will
- Decide upon a design approach
- Design an online learning environment
- Evaluate the process of building learning environment
The objectives for modules 2 were designed to be a lower level and used the action verbs of describe, identify, and explain. Ten hours later the progression of the objectives moved from a comprehension level to a synthesis level and learners were making decisions, designing learning environments, and evaluating their processes.

Reflection Activity
As educators, it is imperative that we level objectives to match the experience and expertise of learners to enhance their learning experience. Can you think of a time when you engaged in a learning activity (either voluntary or mandatory) where the objectives and/or the level of instruction were much too high or too low? How did you feel? What could you have done to address the situation and improve your experience?
This website is maintained by the University of Maryland School of Nursing (UMSON) Office of Learning Technologies. The UMSON logo and all other contents of this website are the sole property of UMSON and may not be used for any purpose without prior written consent. Links to other websites do not constitute or imply an endorsement of those sites, their content, or their products and services. Please send comments, corrections, and link improvements to nrsonline@umaryland.edu.