Online Course
NRSG 780 - Health Promotion and Population Health
Module 8: Program Planning Essentials and Models
Core Functions and the Public Health System
Definition of Public Health:
“What we as a society do collectively to assure the conditions in which people can be healthy”
Exercise
Watch this video to learn more about public health’s role in improving the health status of the United States to in one generation.
Consider the following questions: (click on the question to see the answer)
- Do you think that this video is effective?
- What is missing in this video?
- Answer:
- How to plan and implement the programs identified
P5 - A Public Health Approach
Five key elements in a public health approach to addressing population health issues:
- Populations
Target for intervention: the country as a whole; a specific state, county, city, neighborhood or specific group such as people at risk or with a particular disease
- Prevention
Prevention Levels
- Primary
- Secondary
- Tertiary
Prevention Strategies
High-risk: focuses on identifying the relatively small number of individuals who are at high risk in order to reduce their risk factor(s) and subsequent development of disease
Population-based: focuses on changing behavior in large numbers of people, most of whom have low or no risk at present, in order to prevent the development of risk factors and disease
- Partnerships
- Activities undertaken within the formal structure of government
- Associated efforts of private and voluntary organizations and individuals
- Priorities
Resources are limited, therefore priorities must be established
- Public Health Workforce
- A competent public health and personal health care workforce requires:
- Providing education and training for personnel
- Licensing professionals and certifying facilities including regular verification and inspection follow-ups
- Continuing quality improvement and life-long learning within all licensure/certification programs
- Partnering with professional training programs to assure community-relevant learning experiences
- Assuring continuing education in management and leadership for administrators and executives
- A competent public health and personal health care workforce requires:
Public Health Obligations of Government
- Prevent epidemics and the spread of disease
- Protect against environmental hazards
- Prevent injuries
- Promote and encourage healthy behaviors
- Respond to disasters and assist communities in recovery
- Assure the quality and accessibility of health services
Core Functions of Government in Public Health
- Assessment—identification of problems
- Policy Development—mobilization of necessary efforts and resources
- Assurance—vital conditions are in place so that crucial services can be received
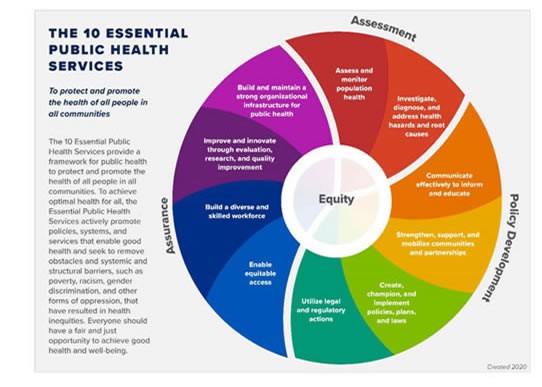
Source: https://www.cdc.gov/publichealthgateway/images/publichealthservices/10-essential-public-health-services.jpg?noicon
Assessment
- Assess and monitor population health
- Investigate, diagnose, and address health hazards and root causes
Policy Development
- Communicate effectively to inform and educate
- Strengthen, support, and mobilize communities and partnerships
- Create, champion, and implement policies, plans, and laws
- Utilize legal and regulatory actions
Assurance
- Enable equitable access
- Build a diverse and skilled workforce
- Improve and innovate through evaluation, research, and quality improvement
- Build and maintain a strong organizational infrastructure for public health
The Public Health System
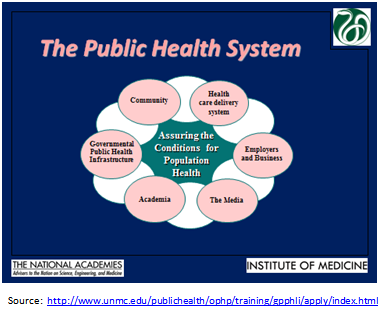
- THE SYSTEM BACKBONE: Governmental Public Health Infrastructure
- Community
- Health care delivery system
- Employers and Business
- The Media
- Academia (public health and health sciences)
Partnerships are expanding in public health and the system is growing more complex as we tackle new problems.
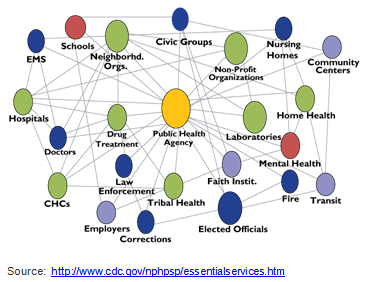
Public health systems are commonly defined as “all public, private, and voluntary entities that contribute to the delivery of essential public health services within a jurisdiction.” This concept ensures that all entities’ contributions to the health and well-being of the community or state are recognized in assessing the provision of public health services.
The public health system includes:- Public health agencies at state and local levels
- Healthcare provider
- Public safety agencies
- Human service and charity organizations
- Education and youth development organizations
- Recreation and arts-related organizations
- Economic and philanthropic organizations
- Environmental agencies and organizations
This website is maintained by the University of Maryland School of Nursing (UMSON) Office of Learning Technologies. The UMSON logo and all other contents of this website are the sole property of UMSON and may not be used for any purpose without prior written consent. Links to other websites do not constitute or imply an endorsement of those sites, their content, or their products and services. Please send comments, corrections, and link improvements to nrsonline@umaryland.edu.