Online Course
Nurs 690 Managerial Health Finance
Module 4: Quality and Cost of Health Care
cost of health care
Health spending in the U.S. increased by 4.3% in 2016 to $3.3 trillion or $10,348 per capita. This growth rate is lower than what was observed in 2015 (5.8%) and 2014 (5.1%) and closer to the growth rates over the 5-year period ending in 2013 which averaged 3.8% per year.
The deceleration in spending occurred almost across the board for many types of health care services and in many programs. This can be attributed to the leveling off of spending growth in 2016 after relatively high growth rates during the implementation of the Affordable Care Act in 2014 and 2015.
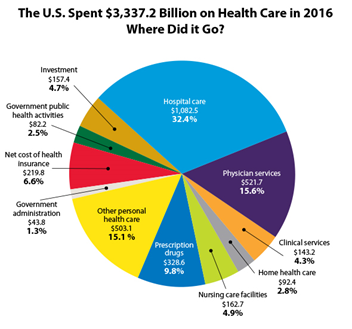
The United States spent $3,337.2 billion on health care in 2016. This spending can be broken down into the following categories:
- Hospital care
- Physician services
- Clinical services
- Prescription drugs
- Nursing care facilities
- Home health care
- Other personal health care costs
- Government administration: includes all administrative costs associated with insuring individuals in health insurance programs
- Net cost of health insurance: this is the difference between health insurance expenditures and benefits incurred and includes administrative costs, additions to reserves, rate credits and dividends, premium taxes and fees, and net underwriting gains or losses
- Government public health activities
- Investment spending
This website is maintained by the University of Maryland School of Nursing (UMSON) Office of Learning Technologies. The UMSON logo and all other contents of this website are the sole property of UMSON and may not be used for any purpose without prior written consent. Links to other websites do not constitute or imply an endorsement of those sites, their content, or their products and services. Please send comments, corrections, and link improvements to nrsonline@umaryland.edu.