Online Course
NDNP 819: Advanced Health Assessment Across the Lifespan
Module: Geriatrics
History
The components of a comprehensive geriatric assessment include medical status, functional capabilities, and psychosocial status. There can be challenges in taking a health history with an older adult. These include sensory impairment (hearing, vision, etc.), restricted mobility, slowed response time/communication difficulties (aphasia), cognitive impairment, and tendency to underreport or minimize symptoms, lengthy medical histories and disease presentation in an atypical fashion.
Strategies to help in getting information include scheduling more than one session for the initial patient history. By having patients bring their medications and supplements in a brown bag and getting collateral history from family/caregivers provides a lot of information. It helps to minimize the impact of sensory deficits (adequate lighting, minimize ambient noise, interruptions) and structure the interview to overcome patients’ disability (ex. yes or no questions for an aphasic patient, attention to non-verbal cues). BE OBSERVANT!!! You can integrate a functional assessment into the exam (see Subtopic 2 for more information).
Just like any patient, you would introduce yourself and address the patient respectfully. It is important to face the patient directly (as oppose to typing in a computer without direct eye contact). Speak slowly and allow the patient time to answer the questions. Using other tools, such as writing in large print and be aware of possible low health literacy to improve self management skills, adherence, and use of preventative services.
PMH includes: previous surgical procedures, major illnesses and hospitalizations, previous transfusions, and TB history and testing
Medications: “What are you taking? How often? Why are you taking them?” Watch for CNS depressants in older adults due to fall risks!
FH may be difficult to collect especially if asking about grandparents in older adults. Doesn’t mean you don’t ask, but recognize you may have more success with asking about siblings and parents
SH includes home/living arrangements, relationship with family & friends, expectations of family/caregivers, economic status, ability to perform ADLs, social activities/hobbies/past occupation, spiritual/religious, transportation and advanced directives. Assessment of elder abuse using these SAFE questions:
- S - Do you feel Safe at home? What Stress do you feel in your relationship?
- A - Do you feel Afraid or have you been Abused by any of your caregivers?
- F - Are there any Family or Friends that you could ask for help or support?
- E – Do you have a safe place to go in case of an Emergency? Is it an Emergency now?
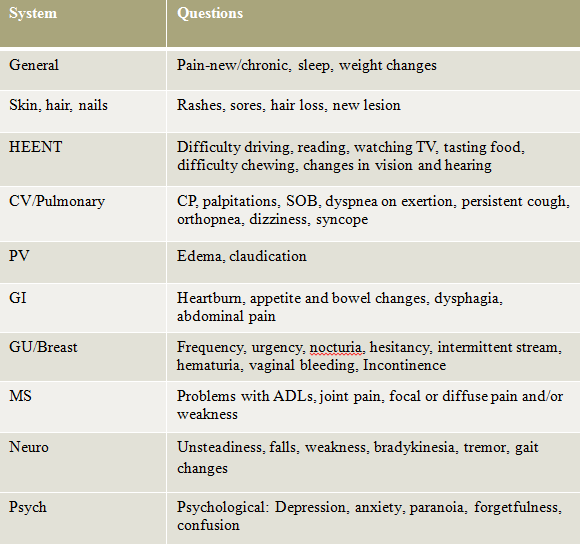
ROS questions that are key for older adults include:
This website is maintained by the University of Maryland School of Nursing (UMSON) Office of Learning Technologies. The UMSON logo and all other contents of this website are the sole property of UMSON and may not be used for any purpose without prior written consent. Links to other websites do not constitute or imply an endorsement of those sites, their content, or their products and services. Please send comments, corrections, and link improvements to nrsonline@umaryland.edu.