Online Course
NDNP 803 - Executive Leadership and Healthcare Economics
Module 12: Reforming Health Care in Maryland
Moving Forward
Maryland’s All-Payer Model Agreement was approved by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) on January 10, 2014. The Health Services Cost Review Commission (HSCRC) is now in the process of implementation. The model grants Maryland broad discretion in regulating Medicare hospital revenue within a rigorous per capita expenditure limit under the existing statutory authority of the HSCRC. The model builds on decades of innovation and equity in health care payment and delivery by modernizing our "all-payer" rate setting system for hospital services. The shared goal is a health care system that enhances patient care, improves health outcomes, and lowers costs.
Under this model, Maryland hospitals committed to achieving significant quality improvements, including reductions in Maryland hospitals’ 30-day hospital readmissions rate and hospital acquired conditions rate. Maryland limited all-payer annual per capita hospital growth, including inpatient and outpatient care, to 3.58 percent, below historical trends. Maryland also limited annual Medicare per capita hospital cost growth to a rate lower than the national annual per capita growth rate per year for 2015-2018. This opportunity is available through the authority of the Innovation Center, which was created by the Affordable Care Act to test payment and service delivery models.
Having successfully met the criteria set forth in the All-Payer Model, Maryland began the Total Cost of Care (TCOC) Model in January 2019.
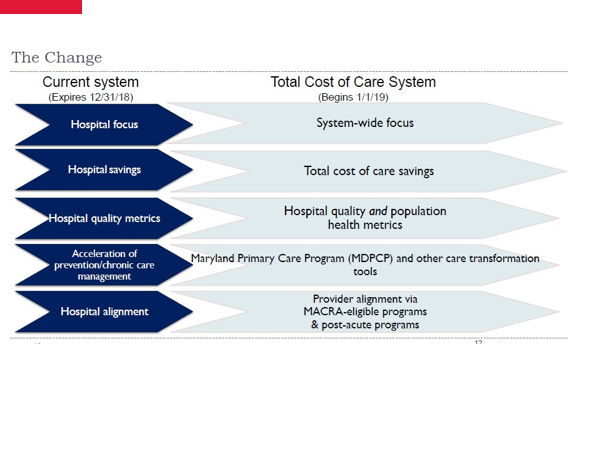
There are several components in the TCOC model including Maryland Primary Care Program (MDPCP) that provides incentives to practices who join into the model.
The MDPCP aims to transform primary care in Maryland, increasing practitioners’ capacity to
provide comprehensive primary care. For the purposes of the Model, comprehensive primary
care is defined as meeting the following five Comprehensive Primary Care Functions of
Advanced Primary Care:
● Care Management
● Access and Continuity
● Planned Care for Health Outcomes
● Beneficiary and Caregiver Experience
● Comprehensiveness and Coordination Across the Continuum of Care.
Complete information about the MDPCM can be found in the document below:
https://innovation.cms.gov/files/x/mdtcocm-rfa.pdf
Another important part of the TCOC model is the quality program that included hospital quality and population health metrics. This will be covered in module 13.
This website is maintained by the University of Maryland School of Nursing (UMSON) Office of Learning Technologies. The UMSON logo and all other contents of this website are the sole property of UMSON and may not be used for any purpose without prior written consent. Links to other websites do not constitute or imply an endorsement of those sites, their content, or their products and services. Please send comments, corrections, and link improvements to nrsonline@umaryland.edu.